- Published on
sql_mysql_常用操作
数据库版本 排名 https://db-engines.com/en/ranking
mysql下载 https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/
修改系统初始化密码:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED by 'root123';
linux下下载mysql
Guide for Install MySQL on Centos7 https://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql-yum-repo-quick-guide/en/
Guide for install MySQL on Ubuntu https://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql-apt-repo-quick-guide/en/
Database 操作
增:create database <name>; ;
删: drop database <name>;
使用:use <database_name>;
查看所有数据库 : show databases;
查看当前正在使用的数据库: select database();
可以更改
;作为sql语句的结尾,delimiter $$
table
table
column
table的相关操作
show tables; # 展示 database所有table
show columns from <table_name>;
desc <table_name>; # 查看table
drop table <table_name>;
create table person (name varchar(20), phone varchar(20), age int);
# 不为空
create table person (name varchar(20) NOT NULL, phone varchar(20), age int);
# default
create table person (name varchar(20) NOT NULL, phone varchar(20), age int default 18);
# primary key 不能为空
create table person (name varchar(20) NOT NULL, phone varchar(20), age int default 18, primary key (phone));
create table person (id int auto_increment, name varchar(20) NOT NULL, phone varchar(20), age int default 18, primary key (id)); # auto_increment
# unique
create table person (name varchar(20) NOT NULL, phone varchar(20) UNIQUE, age int default 18);
primary key (a,b) # 联合主键
Column如果设置成AUTO_INCREMENT,则这个Column必须同时是一个key,即PRIMARY KEY 或者 UNIQUE都可以
emplyee number, birth of date, first name, last name, gender , hired date
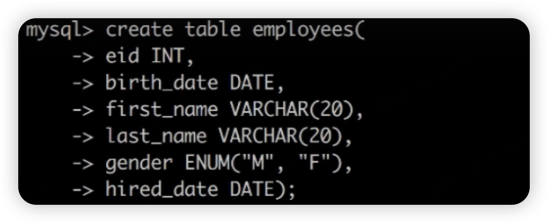
create table if not exists employees (
eid int auto_increment primary key,
brith_date date not null,
first_name varchar(20) not null,
last_name varchar(20) not null,
gender Enum('M','F') not null,
hired_date Date not null default '2000-01-01',
);
数据插入
# 插入单个
insert into table_name(column1, column2) values (column1_value, columns2_value);
# 插入多个
insert into table_name(column1, column2) values (column1_value, columns2_value), (column1_value, columns2_value);
columns注意顺序
# 查看插入的语句
select * from table_name;
# 查看某几个column
select column1_name, column2_name from table_name;
# select 使用别名
select column1_name as new_name, column2_name from table_name;
修改表
ALTER TABLE <表名> ADD <新字段名><数据类型>[约束条件];
ALTER TABLE student ADD age INT(4); # 默认在末尾
ALTER TABLE student ADD stuId INT(4) FIRST; # 在开头添加
ALTER TABLE student ADD stuno INT(11) AFTER name; # 指定column后添加
# 修改表中column类型
alter table user modify username varchar(16);
CRUD
create read update delete
where语句进行数据筛选
select * from employee where title="Software Engineer" or salary="4750";
select * from employee where not title="Software Engineer";
update
update employee set salary=10000 where title="Software Architect";
update employee set salary=10000,title="123" where title="Software Architect"; # 注意使用where
delete
delete from table_name where ""="",
练习
select title, director_name, imdb_score from movie;
select * from movie where title_year="2012" and content_rating="PG-13";
select * from movie where not country="USA";
select * from movie where director_name="Peter Jackson" or director_name="Christopher Nolan";
update movie set imdb_score=9 where director_name="Christopher Nolan";
delete from movie where imdb_score < 6;
delete from movie where title_year=2006;
字符串操作
字符串:拼接,剪辑,反转,长度,大小写
# 拼接
select concat(first_name, ", ", last_name) as fullname from employee;
select concat_ws("-", first_name, last_name) from employee; # 第一个参数 拼接符
# 剪切
select substring("Hello World",1,4) # 第1到第4个字符 Hell
select substring("Hello World",7) # 从第7个开始到最后一个 World
select substring("Hello World",-3) # 从-3到最后 rld # substr 简写
# replace
select replace("Hello World", "World", "Mysql")
# reverse
select reverse("Hello World");
# char_length
select char_length("Hello World") # 11
select upper("Hello World");
select lower("Hello world");
对select数据进行改造
对select 返回的数据进行排序order by
select * from employee order by id; # 默认从低到高
select * from employee order by id desc; # 降序 从高到低
select first_name, last_name order by 2; # 按照last name进行排序
select first_name, last_name order by 2,1; # 按照last name进行排序
限制select 返回数据的数量 limit
select * from employee limit 5; # 返回前5个
select * from employee limit 2,4; # 返回2-4记录
select * from employee limit 2,18446744073709551615; # 查询第二条之后的所有数据
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/select.html
进行select结果的模糊搜索 like
select * from employee where last_name like "C%" # 以C开头的字符
select * from employee where last_name like "%C%" # 包含C的
select * from employee where last_name like "%C" # C结尾的
select * from employee where last_name like "__C" # 长度是3,以C结尾
select * from employee where last_name like "____" # 长度是4
select * from employee where last_name like "%\%%" # 转义 包含%
# 如上匹配时不区分大小写的
分组,聚合
distinct 唯一值
select count(distinct title) from employee; # 返回 title的个数(没有重复值)
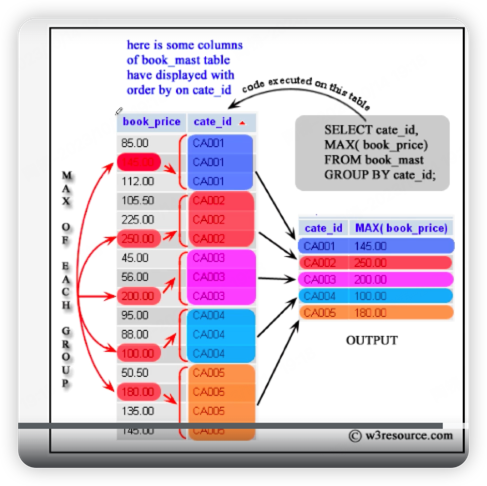
Group by
select title from employee group by title; # 结果如下图
#找到每个职位最大的salary max / min, 对Date 数据类型也可以进行 max min操作
select title, max(salary) from employee group by title;
# 找到所有人的平均薪水和总薪水 , 有了avg和sum之后就不允许再有其他column
select avg(salary), sum(salary) from employee;
# 按照title进行group by
select title, sum(salary) from employee group by title;
having
# where 的过滤是对原始数据的过滤
select title, count(*) from employee where title="" group by title;
select title, count(*) from employee group by title where title=""; # 如果这样会出错
# 对聚合以后的值进行过滤 having, having 也可以放在 group by前。
select title, count(*) from employee group by title having title="Engineer";
练习:
# 获得导演最多电影的前5位导演
select director_name, count(title) from movie group by director_name order by count(title) desc limit 5;
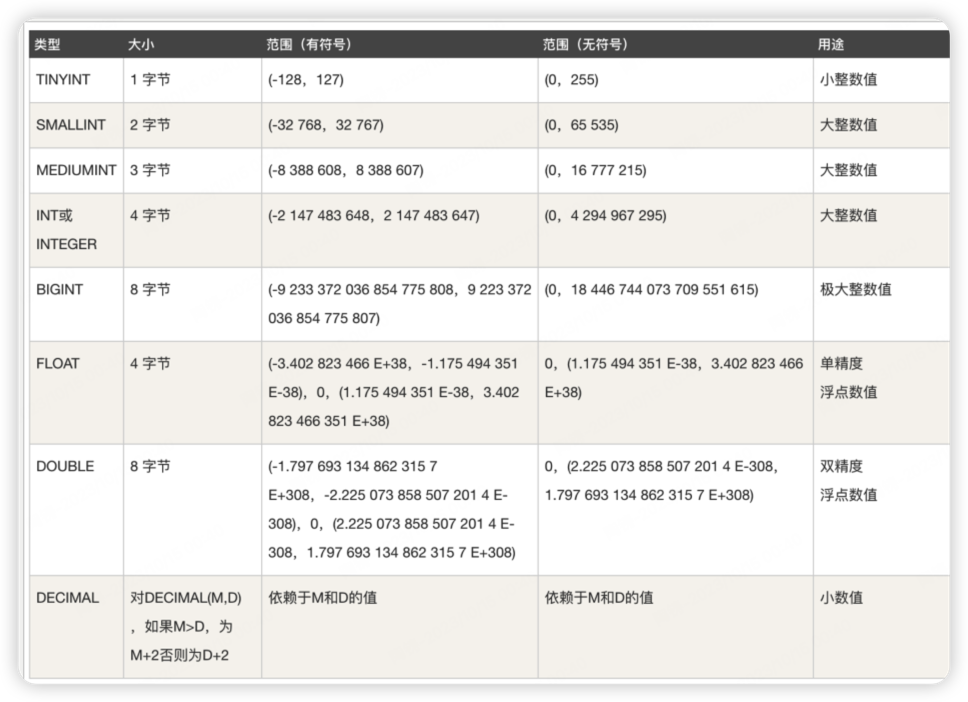
数据类型
数值类型
Integer Types (Exact Value) - INTEGER, INT, SMALLINT, TINYINT, MEDIUMINT, BIGINT
Fixed-Point Types (Exact Value) - DECIMAL, NUMERIC 确定浮点位数
Floating-Point Types (Approximate Value) - FLOAT, DOUBLE 浮点数类型,小数点不固定
Bit-Value Type - BIT 二进制 比如 1101
integer
Exact numeric
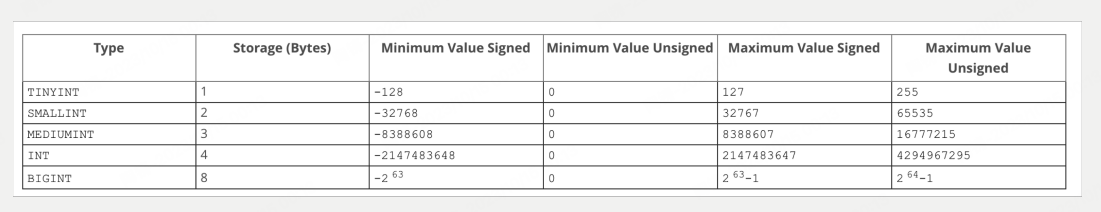
create table demo2 (price int unsigned) # 无符号
Fixed point types
Exact numeric
salary decimal(5,2) # 5位数字,其他小数位2位, 整数位3位
create table demo2 (salary decimal(5,2)) # 小数位数会四舍五入,整数位大于3位会报错。
show warnings; # 查看warnings日志。
floating-point
approximate numeric
FLOAT 4字节
DOUBLE 8字节
对于精确的数值存储需要采用dicimal
Bit
select a+0 from table_name; # 显示10进制
select bin(a+0) from table_name; #显示2进制
select hex(a+0) from table_name; #显示16进制
insert into test4 values(b'111') # 直接插入2进制
insert into test4 values(2) # 直接插入10进制
日期和时间类型
DATE
DATE values in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. The supported range is '1000-01-01' to '9999- 12-31’.
create table test(a DATE);
insert into test(a) values("2022-10-10")
TIME
也可以表示时间间隔
HHH:MM:SS
range from '-838:59:59' to'838:59:59'
insert into test(a) values("10:10:35") # 10小时10分35秒
insert into test(a) values("10:10") # 10小时10分
insert into test(a) values("1010") # 10分10秒
insert into test(a) values("35") # 35秒
YEAR
YEAR(4) and has a display width of four characters.
– As a 4-digit number in the range 1901 to 2155,如果插入1900 就会报错
As a 4-digit string in the range '1901' to '2155'.
– As a 1- or 2-digit number in the range 1 to 99. MySQL converts values in the ranges 1 to 69 and 70 to 99 toYEAR values in the ranges 2001 to 2069 and 1970 to 1999.
– As a 1- or 2-digit string in the range '0' to '99'. MySQL converts values in the ranges '0' to '69' and '70' to '99' toYEAR values in the ranges 2000 to 2069 and 1970 to 1999.
– The result of inserting a numeric 0 has a display value of 0000 and an internal value of 0000. To insert zero and have it be interpreted as 2000, specify it as a string '0'or '00'.
DATETIME
格式 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'
范围 '1000-01-01 00:00:00' to '9999-12-31 23:59:59'.
TIMESTAMP
范围: 1970-01-01 00:00:01' UTC to '2038-01-19 03:14:07'UTC.
datetime 和 timestamp区别
- timestamp会随着时区的变化而变化,Datetime不会变
- timestamp是4个字节,datetime是8个字节
- 范围不同
- timestamp 索引比datetime快
select NOW(); # 获取当前时间
create table test(a datetime default now() on update now())
# 修改mysql的timezone
show variables like "%time_zone%";
set time_zone="-12:00" # 负12小时
# 练习
DATE_FORMAT(date, "%D %M %Y")
12th October 2022
字符类型
CAHR VARCHAR
CHAR fixed length string (0-255) 长度固定
VARCHAR variable-length strings (0-65535)
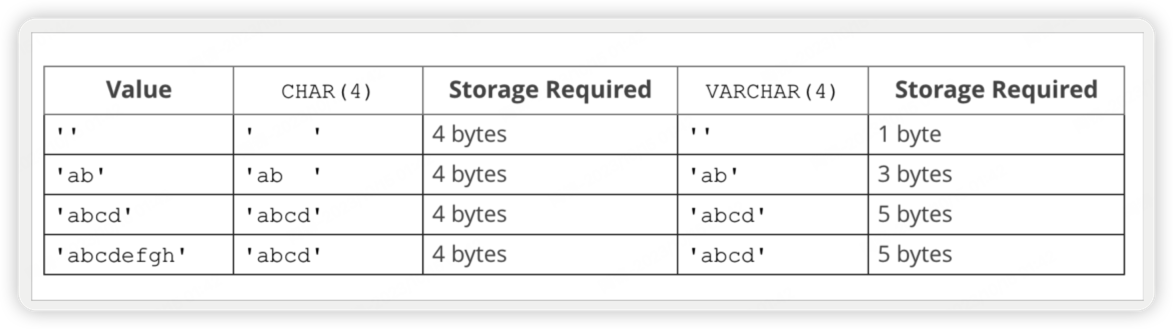
varchar 更新效率不高,因为存储空间是动态的。
BINARY VARBINARH
BLOB TEXT
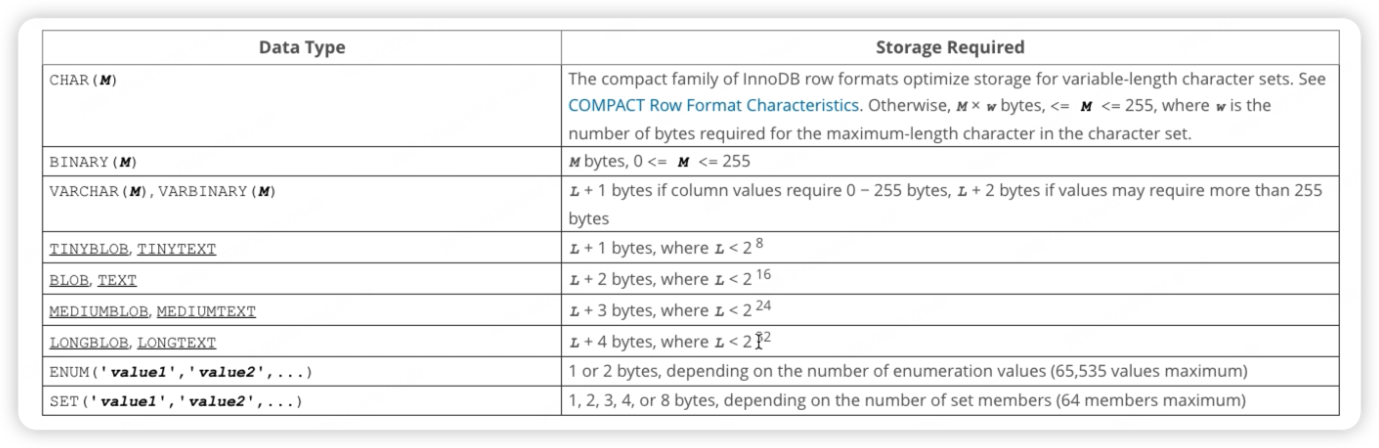
当对长文本进行排序时可以使用 max_sort_length 来控制排序使用的文本长度。
set max_sort_length = 2000;
select id, comment from t order by comment;
ENUM
ENUM("男", "女")
# ENUM中的值有索引,效率比varchar高。
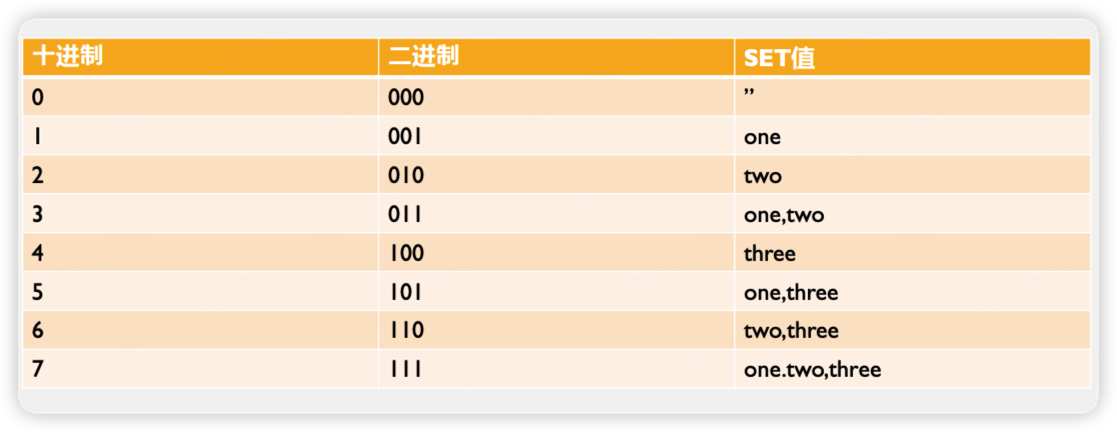
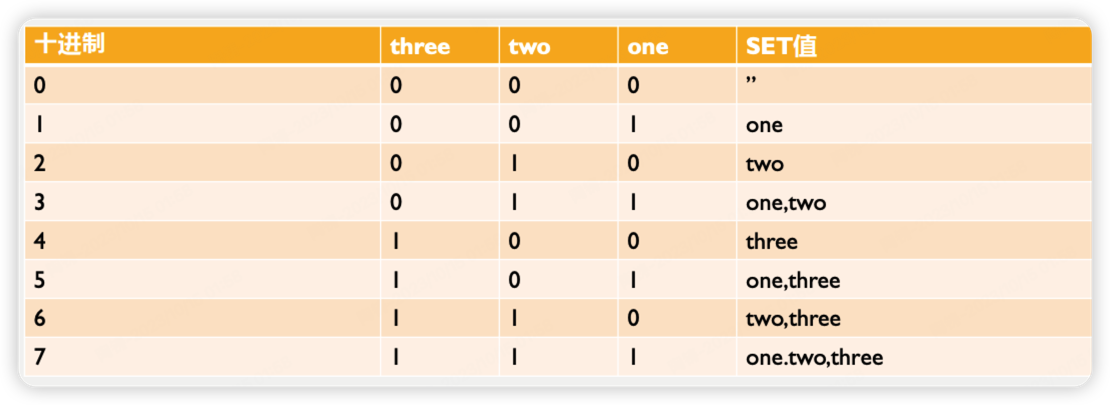
SET
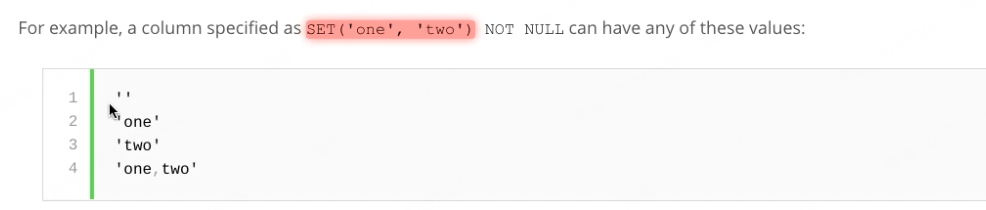
create table set1(a set("one","two","three"))
insert into set1 values(1)
逻辑操作符
等于 =
不等于 !=
like / not like
like "%T%"
严格大小写: like binary "%T%"
# 创建表时声明大小写敏感
create table test2(name varchar(100) binary)
大于,小于,大于等于,小于等于 > < >= <=
and or
between and (连续的空间)
where salary>=6000 and salary<=8000
# ==相等
where salary between 6000 and 8000;
in / not in(离散的点)
where salary in (5000, 6000, 7000);
# ==等于
where salary=5000 or salary=6000 or salary=7000;
case statement
# 如果 salary 小于七千
select name,title,salary,
case # 产生新的一列
when salary>=7000 then "high"
when title like "%A%" then "2"
else 'low'
end as tag
from employee order by salary;
内置函数
待补充 内置函数ppt
关系
一对多
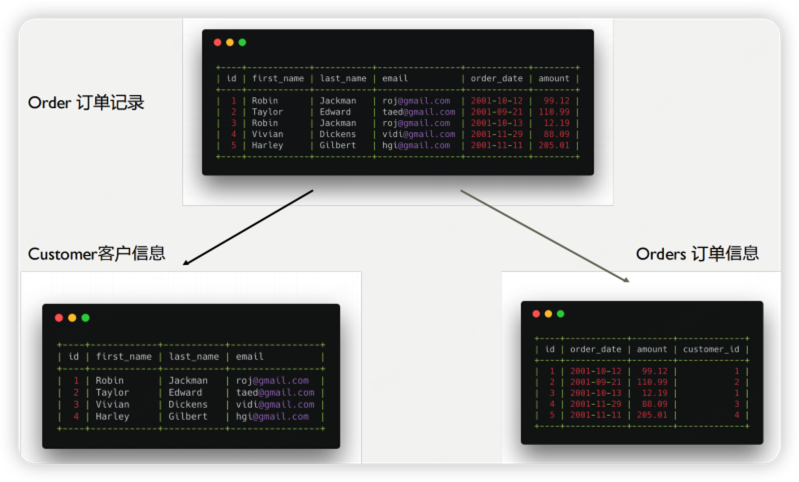
select * from orders where customer_id=(select id from customs where emial="1.qq.com")
# foreign key
create table orders(
id int auto_increment primary key,
order_data date,
amount decimal(8,2),
customer_id int,
foreign key(customer_id)
references customers(id), # customers 另一个表名
on delete CASCADE # 当customers 删除一个id时候,custom对应order也会删除
)
# 插入非法id的时候,mysql会帮我们校验
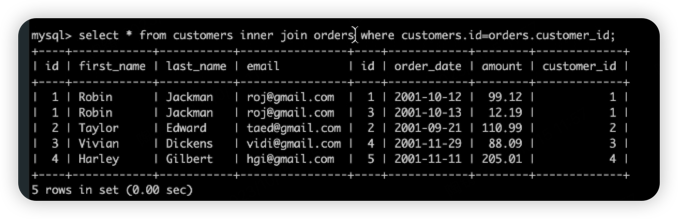
inner join,取两张表重合的部分。
如果顾客表中一个顾客没有订单,则inner join不会出现该顾客,如果要出现需要left join
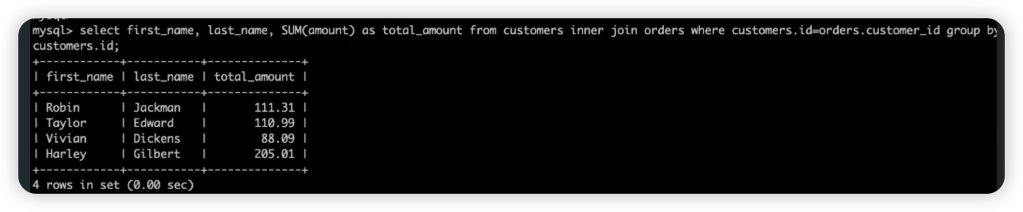
left join
左边的完整信息 + 另一张表的重叠信息。
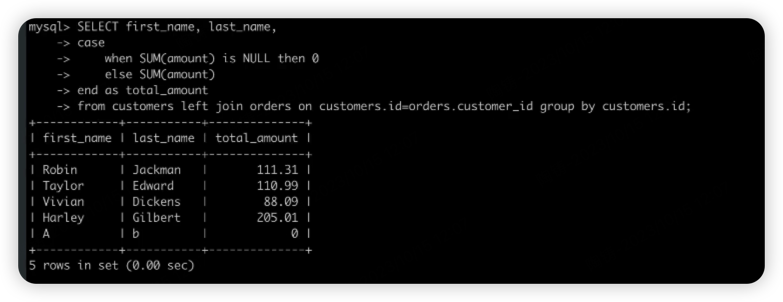
ifnull函数可以方便的实现上面的语句
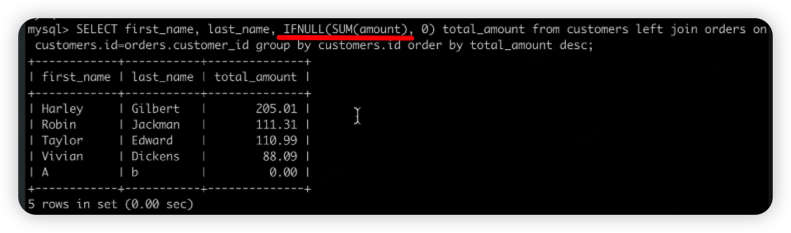
right join
和left join相反
多对多

mysql编码
插入中文报错
create database test default charset=utf8 collate=utf8_general_ci;
create database demo_sm default charset=utf8 collate=utf8_general_ci;
# 更改
alter database test charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci
# 更改table编码
alter table tablename convert to character set utf8;
# 查看数据库编码
show create database demo;
Python sqlalchemy
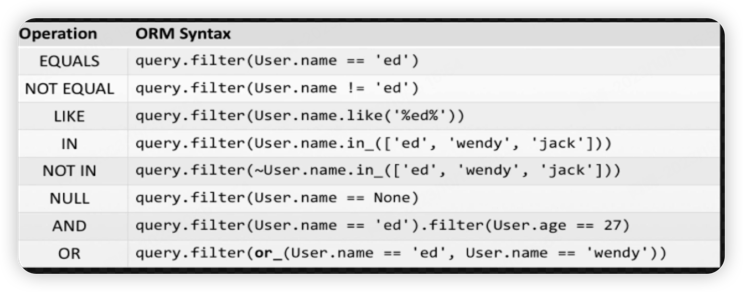
import sqlalchemy as sa
from movie import Movie, BASE
engine = sa.create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:root@localhost:3306/demo", echo=True)
Session = sa.orm.sessionmaker(bind=engine)
BASE.metadata.create_all(engine)
s = Session()
# SELECT
# director_name, COUNT(title)
# FROM movie GROUP BY director_name ORDER BY COUNT(title) DESC LIMIT 10;
m1 = s.query(
Movie.director_name, sa.func.count(Movie.title)
).group_by(Movie.director_name).order_by(sa.func.count(Movie.title).desc()).limit(10)
for m in m1:
print(m)
# SELECT
# director_name, SUM(gross)
# FROM movie GROUP BY director_name ORDER BY SUM(gross) DESC LIMIT 10;
m2 = s.query(
Movie.director_name,
sa.func.sum(Movie.gross)
).group_by(Movie.director_name).order_by(sa.func.sum(Movie.gross).desc()).limit(10)
for m in m2:
print(m)
"""
SELECT
tweet
FROM tweet INNER JOIN user
ON user.id=tweet.user_id WHERE user.username="test2"
"""
ts = s.query(Tweet).join(
User,
User.id == Tweet.user_id
).filter(User.username == 'test2')